The simplest and most obvious approach to solving the flow equations is Euler's method. I review it here only because it is used in spreadsheet type models and it so aptly demonstrates the problem of model instability.
The equations of the trivial form of the problem are, again...
![]()
Euler's method gives us the values of V at time ![]() assuming we know
the values of V at time t.
assuming we know
the values of V at time t.
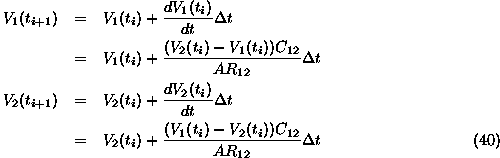
Where ![]()
Now it is instructive to note what is actually used in the calculation of the next time step.
Ideally, the result should not depend on the value of the time step. If we take smaller time steps, the changes are smaller, but we take more steps, thus hopefully completely canceling out any effect the actual value of the time step may have. I must emphasize this further. Physically speaking, the lake does not have a time step, therefore this time step is purely an artifact of the way we solve the equations, and does not have anything to do with reality.
Again, where does Euler's method come from? It comes from Taylor's theorem. Taylor's
theorem states that for any mathematically "nice-and-smooth" function Y(t),
(where "nice-and-smooth" can be given a highly technical and precise meaning),
the following is true.
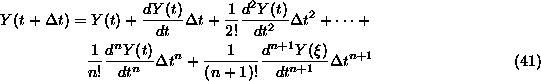
Where ![]() is an unknown value anywhere from t to
is an unknown value anywhere from t to ![]() .
.
Now Euler's method just says, if ![]() is small, and our function's second derivative
V(t) is well-behaved (good boy function), we can ignore terms in
is small, and our function's second derivative
V(t) is well-behaved (good boy function), we can ignore terms in ![]() and higher.
and higher.
So when are we making significant errors? When for some ![]() between t and
between t and ![]() ,
the error
,
the error ![]() is significant. In this trivial case we can easily calculate this error...
is significant. In this trivial case we can easily calculate this error...
Error in a single step of Euler's method
![]()
Where the volumes are evaluated at some time between t and ![]() .
.
From this we can see...