Next: How complex a model Up:
Draft - The water Previous: Verification of the ecosystem
Figure 30 displays mean concentration in the North Lake
cell versus percentage change in various inputs and parameters.
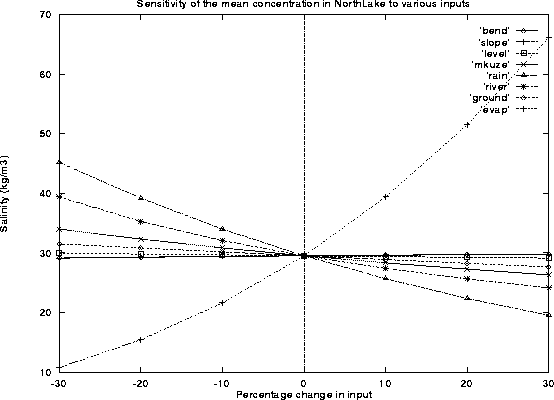
Figure 30: Sensitivity of lake model to changing inputs and parameters.
The inputs and parameters changed are...
- evap
- Total evaporation from the lake surface.
- rain
- Total rainfall directly onto the lake surface.
- river
- Total river inflow to the lake, (including the Mkuze).
- mkuze
- The Mkuze river only.
- ground
- Ground water inflow.
- level
- The effective sea level. This is a function of the estuary mouth parameters. Varying
this effectively varies the depth of the lake.
- slope
- This is a function of the estuary mouth parameters. A high slope corresponds a wide
open, deep, smooth channel, and a low slope to a narrow, shallow, rough channel. Varying
this effective changes the relaxation time of the lake, ie. How long it takes the lake to
drain to the sea. Opening Potters channel is equivalent to increasing this parameter.
- bend
- The non-linearity of the estuary mouth. Varying this changes the lakes response to flood
conditions.
One can clearly see from the Figure 30 that the system
is dominated in order of decreasing importance by...
- Evaporation clearly drives the salinity of the lake. Probably the best way to improve
the accuracy of this simulation would be to get better evaporation data.
- Direct surface rainfall.
- River flow.
All other inputs and parameters have almost neglicable effects on the system.
John Carter
Tue Jun 17 09:50:07 SAT 1997

