Let there be N square sided cells of arbitrary area. Let each cell have an arbitrary
time dependent inflow/outflow and a linear level dependent estuary mouth. Then the
equations are
![]()
Where ![]() is the set of all neighbouring cells of cell i. The Kronecker delta
is the set of all neighbouring cells of cell i. The Kronecker delta ![]() is
1 is if i=1 otherwise 0.
is
1 is if i=1 otherwise 0.
Define matrix ![]() as...
as...
![]()
Define vector V and I as...
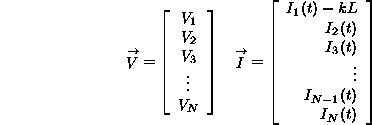
Now the differential equations can be written in matrix form...
![]()
Where A is an N by N matrix, and V is a N vector of volumes and I is an N vector of inflow/outflow functions.
The matrix A can be factored into three matrices...
![]()
Assuming there exists N distinct real eigenvalues of A, then ![]() is the diagonal N
by N matrix of eigenvalues of A, and E is the matrix with the eigenvectors of A as its
columns. Thus..
is the diagonal N
by N matrix of eigenvalues of A, and E is the matrix with the eigenvectors of A as its
columns. Thus..
![]()
Now multiply through by ![]() ...
...
![]()
Define W to be ![]() , and G(t) to be
, and G(t) to be ![]() . Then..
. Then..
![]()
As ![]() is diagonal, the equations are separated thus...
is diagonal, the equations are separated thus...
![]()
Where ![]() is the i'th eigenvalue of
is the i'th eigenvalue of ![]() .
.
The Green's function solution to the equations is..
![]()
Where ![]() is an arbitrary constant of integration.
is an arbitrary constant of integration.
As ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]()
General Green's function solution to the N-Cell problem.
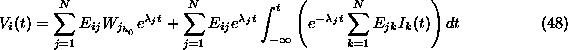
The first summation corresponds to transients that die away. This is how the system varies continuously from the arbitrary initial condition to the long term response to the input given in the second summation.