![]()
The cos of u, the angle between these two displacements can be calculated from the
scalar product...
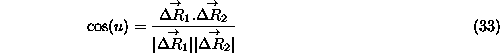
Now by the conform property we can equate the ![]() calculated on the map and
on the surface of the earth. Thus :-
calculated on the map and
on the surface of the earth. Thus :-
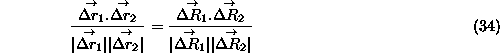
Thus putting all the details in we get...
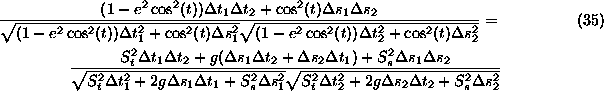
Now as the delta's are small but arbitrary we can set ...
![]()
Then equation (37) becomes...
![]()
Which implies that g=0. Using the definition of g in equation (32) we get the partial differential equation...
![]()
This simplifies equation (37) to ...
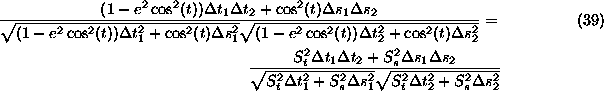
As the delta's are small but arbitrary we can set ![]() then the above becomes...
then the above becomes...
![]()
Squaring both sides and simplifying gives you...
![]()
Which as the terms in ![]() cancel...
cancel...
![]()
Now one can use the result of g=0 to relate ![]() and
and ![]() ...
...
![]()
Thus solving this for ![]() ...
...
![]()
And using it to remove ![]() from equation 43...
from equation 43...
![]()
We can cancel ![]() on either side and simplify...
on either side and simplify...
![]()
Now take square roots of both sides....
![]()
Plugging this into the equation (39) resulting from g=0
gives us...
![]()
We wish to define a map projection whose axis orientation matches standard mathematical practice, and more particularly, matches the ARC/INFO GIS, Y increases with latitude and X increases with longitude eastwards. Thus we choose the sign in (49) to be +ive and the sign in (48) to be -ive.