Referring to equation 1, and figure 10, assume two equal sized square sided cells. Thus the
areas ![]() and the levels
and the levels ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the volume of
the i'th cell.
is the volume of
the i'th cell.
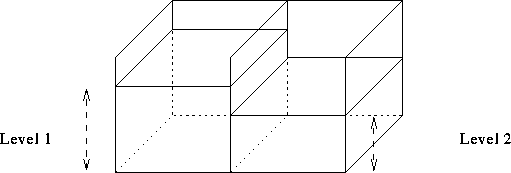
Figure 10: Two square sided cells of equal area.
So the flow from cell 1 to cell 2 is ...
![]()
Assuming no in or out flows, only the inter-cell gravity link...
![]()
Placing this in matrix form...
![]()
Where
![]()
Now find the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of the matrix so that one can diagonalize the
matrix. An eigenvalue ![]() of a matrix B and its corresponding eigenvector
of a matrix B and its corresponding eigenvector ![]() is defined to be
such
is defined to be
such ![]() .
.
Thus the determinant of ![]() must be zero, this gives you the characteristic
polynomial
must be zero, this gives you the characteristic
polynomial ![]()
Solving the characteristic polynomial, we get the eigenvalues ![]() and
and ![]() .
Using these to find the corresponding eigenvectors we get
.
Using these to find the corresponding eigenvectors we get ![]() and
and ![]() thus
we can diagonalize the matrix.
thus
we can diagonalize the matrix.
![]()
Perform a change of variable to variables that are basically the eigenvectors of the
problem. ie let ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Then...
![]()
Thus ![]() is a constant of the system. (No surprise, this is just saying that
is a constant of the system. (No surprise, this is just saying that ![]() , the
total volume of water in the system is conserved.)
, the
total volume of water in the system is conserved.)
And ...
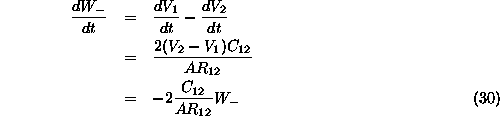
Which is now an equation which we can solve...
![]()
Integrating both sides gives us...
![]()
Where K is an arbitrary constant of integration.
Taking the exponential of both sides and letting ![]() gives us...
gives us...
![]()
Where ![]() is an arbitrary constant of integration to be determined by boundary
conditions.
is an arbitrary constant of integration to be determined by boundary
conditions.
Now reversing the substitution of variables we have...
![]()
![]()
Now at time t=0 we have...
![]()
![]()
Solving for the constants ![]() and
and ![]() we get...
we get...
![]()
![]()
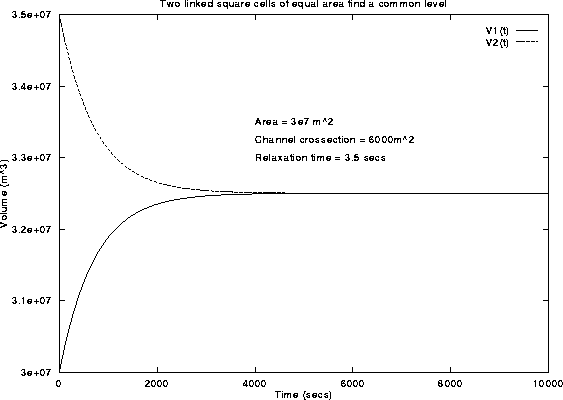
Figure 11: The volumes in two linked cells reach common level. The
parameters are chosen to be similar to the North Lake cell.
Which finally gives us the exact analytic solution for this trivialised problem. See figure 11 for a graphical representation.
Volume of two linked square sided cells of equal area.
So what can we learn from the solution?