| RHP |
South African
River Health Programme |
State of the Rivers Report
Crocodile, Sabie-Sand & Olifants River Systems |

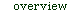


|
|
The Sabie-Sand River System |
|
Catchment overview The Sabie-Sand Catchment covers some 6 320 km2 and forms part of the larger Incomati System, which extends into Swaziland and Mozambique. The Sabie River is the mainstream of the catchment, with the Sand and Marite Rivers acting as major tributaries, and the Mac Mac River being a tertiary drainage. The Sabie River has its source at 2 130 m above mean sea level in the Drakensberg Escarpment, drops into the lowveld and joins the Sand River inside the Kruger National Park.
Mean annual rainfall in the catchment varies between 2 000 mm on the Escarpment to around
|
|
Summary of findings
Move cursor over map and select specific area to view detailed map and Present Ecological State (PES) findings.
|



|