|
Any control programme for alien vegetation
must include the following 3 phases:
- Initial control: drastic reduction of existing population
- Follow-up control: control of seedlings, root suckers and coppice
growth
- Maintenance control: sustain low alien plant numbers with annual
control
MECHANICAL & CHEMICAL METHODS
Where trees cannot be utilised (on steep slopes), do not fell
trees, control them in situ.
Select from the following options:
- Basal bark: Application of suitable herbicide in diesel can
be carried out to the bottom 250mm of the stem. Applications should
be by means of a low pressure, coarse droplet spray from a narrow
angle solid cone nozzle.
- Hand pull: Grip the young plant low down and pull out by hand
(using gloves).
- Ring barking: Bark must be removed from the bottom of the stem
to a height of 0.75-1.0 m. All bark must be removed to below ground
level for good results. Where clean de-barking is not possible
due to crevices in the stem or where exposed roots are present,
a combination of bark removal and basal stem treatments should
be carried out. Bush knives or hatchets should be used for debarking.
- Frill: Using an axe or bush knife. Make angled cuts downward
into the cambium layer through the bark in a ring. Ensure to effect
the cuts around the entire stem and apply herbicide into the cuts.
 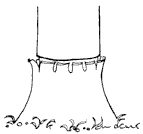
The Frilling Method
Where trees can be felled and removed use chainsaws, bowsaws,
brushcutters or cane knives.
| Management treatments summary guide for terrestrial & aquatic IAPs |
|
American
bramble
Australian myrtle
Barbados gooseberry
Beefwood
Black wattle
Blackwood
Bluegums
Brazilian pepper tree
Bugweed
Cacti spp
Camel thorn bush
Cluster
pine |
Golden wattle
Green wattle
Grey Poplar
Guava
Honey Mesquite / prosopis
Inkberry
Jacaranda
Kudzu
Lantana
Long-leaved wattle
Mauritius
thorn |
Peanut Butter Tree
Port jackson willow
Queen of the night
Red sesbania
Rock Hakea
Rooikrans
Silver wattle
Sisal
Syringa
Triffid weed |
| ...
Click here |
BIOLOGICAL CONTROL
Biocontrol
dossiers
(for 22 species in South Africa)
NOTICE : You'll need
Acrobat Reader to view these files. Download and install
Acrobat Reader here.
Click here to
find out where to obtain Biocontrol Agents
Indigenous Replacement
Plants in the KZN region - (this will open a MS Word
document in a new window)
Activity
sampling
The national Working for Water programme
has been clearing invading alien plants since 1995. The programme
grew from 20 projects in 1996 to over 300 projects currently. This
rapid growth hindered the standardisation of clearing methods and
norms between regions. The result is that Working for Water
has a wide range of efficiency and productivity values across the
country.
The Activity Sampling programme was introduced
to establish realistic norms with regard to clearing methods and
productivity. The programme was initiated with the following
objectives:
- To raise recommendations for increasing productivity in the Working
for Water programme
- To establish realistic norms with regard to person days per
hectare
- To describe clearing methods used
- To define size and density classes
- To establish standardised clearing methods per species and
per operation
The Mondi Forests Work Study Department is
responsible for the implementation of the activity sampling
programme in each region. Evaluators are allowed to visit teams in
the field and to make accurate assessments as to where there might
be areas where improvement could lead to higher productivity.
In specific areas where activity sampling was
done, productivity rose from an average of 65% to more than 80%.
Increases in productivity averages on this scale impact
significantly on projects such as Working for Water.
Consider, for example, the impact a 15% increase in productivity
would have on a project with a budget of R42 million!
Click here to visit the Plant Protection Research Institute
Website: http://www.arc.agric.za/v-arcroot/institutes/ppri/main/home.htm
Relevant Acts dealing with
Invasive Alien Plant Control & Wetland Rehabilitation
Implemention
Applications forms to request Clearing
|